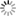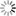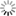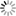Possible life cycle of SARS-CoV-2 and potential intervention strategy

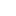
Figure 2. Possible life cycle of SARS-CoV-2 and potential intervention strategy
D'après : Potential Therapeutic Targets and Promising Drugs for Combating SARS-CoV-2. Zhou, Hong et al. May 6, 2020
Schematic diagram showing the possible transmission, infection and pathogenesis cycle of SARS-CoV-2. In the infection phase, SARS-CoV-2 attaches to the cellular receptor via the spike (S) protein or the transmembrane glycoprotein CD147 to enter the host cell by the endosomal pathway. At this point, the S protein is activated and cleaved by transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) to trigger membrane fusion. Then, SARS-CoV-2 releases its nucleocapsid into the cytoplasm to induce translation of ORF1a/b into the large replicase polyproteins 1a (pp1a) and pp1ab and replicates its of genomic RNA. Subsequently, pp1a and pp1ab produce various nonstructural proteins (nsps), in which the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP), Papain-like protease (PLpro) and 3C-like protease (3CLpro) are encoded.These replicases synthesize the full-length negative-sense antigenome template to produce new genomic RNA and further form the assembled virion, which is then released into the extracellular space by exocytosis. Uncontrolled replication promotes SARS-CoV-2 infection, leading to immune disturbances and inflammatory cytokine storms and eventually resulting in multiorgan functional damage, particularly in the lung.